
Does TRT Lead to Gynecomastia?
Does Testosterone Cause Breast Enlargement (Gynecomastia)?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) has become a popular treatment for men experiencing low testosterone levels, a condition that can significantly impact quality of life. While TRT offers numerous benefits, including increased energy, improved mood, and enhanced muscle mass, it has potential side effects. One of the concerns many men have is whether TRT can lead to gynecomastia or the enlargement of male breast tissue. Understanding the relationship between TRT and gynecomastia is crucial for making informed decisions about hormone therapy. This article delves into the causes, mechanisms, and management strategies related to gynecomastia in the context of TRT.
Understanding Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Testosterone Replacement Therapy involves the administration of testosterone to individuals with low levels of this vital hormone. Testosterone is essential for various bodily functions, including the development of male sexual characteristics, maintenance of muscle mass, bone density, and overall mood regulation. Low testosterone levels, a condition known as hypogonadism, can result from aging, medical conditions, or other factors, leading to symptoms like fatigue, decreased libido, and mood swings.
TRT aims to restore testosterone levels to a normal range, thereby alleviating these symptoms and improving overall well-being. The therapy can be administered through injections, patches, gels, or pellets, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. While TRT can significantly enhance quality of life, it is not without potential side effects, one of which is gynecomastia.
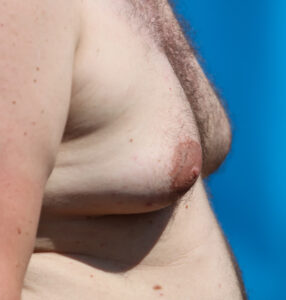
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of male breast tissue. It is a common condition that can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly. Gynecomastia can occur at any age but is particularly prevalent during adolescence and in older men. The condition is typically caused by an imbalance between the hormones testosterone and estrogen. When estrogen levels rise relative to testosterone, breast tissue can develop and enlarge, leading to the characteristic swelling associated with gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia can be a source of psychological distress, affecting self-esteem and body image. While it is usually harmless, persistent or severe cases may require medical intervention. Understanding the factors that contribute to gynecomastia, especially in the context of TRT, is essential for prevention and management.
How Does TRT Potentially Lead to Gynecomastia?
TRT can lead to gynecomastia primarily through the process of aromatization, where testosterone is converted into estrogen by the enzyme aromatase. This increase in estrogen levels can disrupt the hormonal balance, favoring the development of breast tissue. Here’s a closer look at how this process unfolds:
- Aromatization Process: Testosterone naturally converts to estrogen via aromatase enzymes present in various tissues, including fat tissue. When exogenous testosterone is introduced through TRT, the body may convert some of this additional testosterone into estrogen, leading to elevated estrogen levels.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Elevated estrogen levels relative to testosterone create an environment conducive to the growth of breast tissue. Estrogen promotes the development of glandular tissue, which can result in the enlargement of the breasts.
- Feedback Mechanism: TRT can suppress the body’s natural production of testosterone due to the negative feedback mechanism in the endocrine system. Lower endogenous testosterone levels can further tilt the hormonal balance towards estrogen dominance.
- Genetic and Individual Factors: Some individuals may have a higher propensity for aromatization due to genetic factors or higher levels of aromatase enzymes. This predisposition can increase the likelihood of developing gynecomastia while on TRT.
The Role of Estrogen in Gynecomastia
Estrogen plays a pivotal role in the development of gynecomastia. In men, estrogen is present in smaller amounts compared to women, but it is essential for regulating various physiological processes. However, when estrogen levels become too high, it can lead to the proliferation of breast tissue. Here’s how estrogen contributes to gynecomastia:
- Breast Tissue Development: Estrogen stimulates the growth of ductal tissue in the breasts. In excess, this leads to the visible enlargement of the breasts.
- Hormonal Balance: The balance between estrogen and testosterone is crucial for maintaining male secondary sexual characteristics. An imbalance, where estrogen predominates, disrupts this equilibrium and favors breast tissue growth.
- Aromatase Activity: Increased aromatase activity, which converts testosterone to estrogen, exacerbates the estrogen dominance, further promoting gynecomastia.
Understanding the role of estrogen is essential for managing gynecomastia in men undergoing TRT. Strategies to control estrogen levels can mitigate the risk of developing this condition.
Mechanisms of Testosterone Conversion to Estrogen (Aromatization)
Aromatization is the biochemical process through which testosterone is converted into estrogen. This conversion is catalyzed by the enzyme aromatase, which is present in various tissues, including adipose (fat) tissue, the brain, and the testes. The extent of aromatization can be influenced by several factors:
- Body Fat Percentage: Higher levels of body fat are associated with increased aromatase activity, leading to greater conversion of testosterone to estrogen. This is why overweight or obese individuals may be more prone to gynecomastia when on TRT.
- Age: As men age, aromatase activity can increase, contributing to higher estrogen levels and a higher risk of gynecomastia.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic variations can affect the activity of aromatase enzymes, making some individuals more susceptible to estrogen-related side effects.
- Dosage and Administration of TRT: Higher doses of testosterone or certain administration methods can influence the rate of aromatization. Proper dosing under medical supervision can help manage estrogen levels effectively.
Understanding the mechanisms of aromatization helps in devising strategies to prevent and manage gynecomastia in men undergoing TRT.
Factors Influencing the Likelihood of Developing Gynecomastia on TRT
Several factors can influence whether an individual on TRT will develop gynecomastia. These include:
- Dosage of Testosterone: Higher doses of testosterone increase the likelihood of aromatization, thereby raising estrogen levels and the risk of gynecomastia.
- Individual Aromatase Activity: People with higher aromatase activity convert more testosterone into estrogen, increasing their risk.
- Body Composition: Individuals with higher body fat percentages have more aromatase enzymes, leading to greater conversion of testosterone to estrogen.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can play a role in how an individual metabolizes testosterone and estrogen.
- Age: Older men are generally more susceptible to hormonal imbalances due to changes in metabolism and enzyme activity.
- Lifestyle Factors: Alcohol consumption, diet, and exercise can influence hormone levels and aromatase activity.
By recognizing these factors, individuals and healthcare providers can better assess the risk of gynecomastia and take preventive measures accordingly.
How to Prevent or Manage Gynecomastia While on TRT
Preventing and managing gynecomastia involves maintaining a healthy hormonal balance and addressing the factors that contribute to estrogen dominance. Here are several strategies that can help:
- Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs): Medications like anastrozole or letrozole can inhibit the aromatase enzyme, reducing the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. This helps maintain a healthier testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Drugs such as tamoxifen or raloxifene can block estrogen receptors in breast tissue, preventing estrogen from exerting its effects and thereby reducing the risk of gynecomastia.
- Adjusting TRT Dosage: Lowering the dosage of testosterone or adjusting the frequency of administration can help minimize excess testosterone that could be converted into estrogen.
- Monitoring Hormone Levels: Regular blood tests to monitor testosterone and estrogen levels are essential. This allows for timely adjustments in therapy to maintain hormonal balance.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Management: Reducing body fat can decrease aromatase activity and, consequently, estrogen production.
- Diet: A balanced diet that supports hormonal health can be beneficial. Avoiding excessive alcohol and maintaining adequate nutrient intake supports overall hormonal balance.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps manage body weight and can influence hormone levels positively.
- Timing of TRT: Some protocols suggest cycling TRT or using breaks to prevent the accumulation of excess testosterone and subsequent aromatization.
- Natural Supplements: Certain supplements, such as zinc and vitamin D, may support hormone balance, although their effectiveness can vary and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
- Surgical Options: In cases where gynecomastia becomes persistent or severe, surgical intervention may be considered to remove the excess breast tissue.
Alternative Therapies or Strategies
Beyond traditional TRT and the aforementioned management strategies, several alternative approaches can support hormonal balance and reduce the risk of gynecomastia:
- Peptide Therapy: While primarily focused on other aspects of health, some peptide therapies can support hormone regulation and potentially influence estrogen levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider about the integration of peptide therapy with TRT may offer additional benefits.
- Natural Testosterone Boosters: Herbs and natural supplements like fenugreek, ashwagandha, and tribulus terrestris are sometimes used to support testosterone levels naturally, potentially reducing the need for higher doses of TRT.
- Comprehensive Hormone Optimization: A holistic approach to hormone health, addressing not just testosterone but also other hormones like cortisol and thyroid hormones, can support overall balance and reduce side effects like gynecomastia.
The Importance of Medical Supervision
Managing TRT and preventing gynecomastia requires careful medical supervision. Self-administering testosterone without professional guidance can lead to imbalances and increase the risk of adverse effects. Here’s why medical supervision is essential:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Healthcare providers can tailor TRT protocols based on individual needs, minimizing the risk of hormone imbalances.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing blood tests and assessments ensure that testosterone and estrogen levels remain within optimal ranges, allowing for timely adjustments.
- Managing Side Effects: Early detection of side effects like gynecomastia allows for prompt intervention, preventing the condition from becoming more severe.
- Comprehensive Care: Medical professionals can address other health aspects that may influence hormone levels, providing a more holistic approach to treatment.
Conclusion
TRT offers significant benefits for men suffering from low testosterone, enhancing their quality of life through improved energy, mood, and physical health. However, like any medical treatment, it comes with potential side effects, one of the most concerning being gynecomastia. Understanding the mechanisms behind TRT-induced gynecomastia, such as aromatization and hormonal imbalance, is crucial for prevention and management. By working closely with healthcare professionals, adjusting dosages, and employing strategies like aromatase inhibitors or lifestyle modifications, men can mitigate the risk of developing gynecomastia while still reaping the benefits of TRT.
Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider and regularly monitoring your hormone levels are essential steps in ensuring the safe and effective use of TRT. If you’re considering testosterone replacement therapy or are currently undergoing TRT and concerned about gynecomastia, it’s important to seek professional guidance.
At Vitality Aesthetic & Regenerative Medicine, we understand the complexities of hormone therapy and the concerns that come with it, including the risk of gynecomastia. Our experienced team is dedicated to providing personalized TRT plans tailored to your unique needs, ensuring that you achieve optimal hormone balance while minimizing potential side effects. Whether you’re considering TRT for the first time or looking to adjust your current regimen, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Don’t let concerns about gynecomastia hold you back from experiencing the benefits of testosterone therapy. Contact Vitality Aesthetic & Regenerative Medicine today to schedule a consultation. Our knowledgeable staff is ready to answer any questions you may have and guide you toward a healthier, more vibrant life. Take control of your hormonal health and embrace the vitality you deserve!

